At Spinifex Energy, we’ve seen a surge in solar panel installations worldwide. This growth brings a new challenge: the need for effective commercial solar panel recycling.
As panels reach the end of their lifespan, proper disposal becomes crucial to minimize environmental impact and recover valuable materials.
In this post, we’ll explore the current methods, challenges, and opportunities in solar panel recycling, and why it’s vital for the industry’s sustainable future.
Why Solar Panel Recycling Matters Now
The Solar Boom and Its Consequences
The solar energy industry is experiencing unprecedented growth. The International Energy Agency predicts global solar capacity will triple by 2027, reaching 1,500 GW. This rapid expansion brings a new challenge: managing the end-of-life cycle of solar panels.
Understanding the Solar Panel Lifecycle
Solar panels typically last 25-30 years. However, efficiency decreases over time, prompting earlier replacements. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory estimates that by 2030, the U.S. alone will accumulate about 1 million tons of solar panel waste.
Environmental Risks of Improper Disposal
Improper disposal of solar panels poses significant environmental risks. These panels contain toxic materials (such as lead, cadmium, and selenium). When panels end up in landfills, these harmful substances can leach into soil and groundwater.
The Treasure Trove of Recyclable Materials
Solar panels are rich in valuable materials. Each panel contains about 80% glass, plus aluminum, copper, and small amounts of silver and silicon. The International Renewable Energy Agency projects that recycled materials from solar panels could be worth $15 billion by 2050.
Economic Opportunities in Recycling
The growing need for solar panel recycling creates new business opportunities. Companies specializing in panel recycling are emerging, promising both environmental benefits and economic gains. For example, Veolia (a global waste management company) has opened Europe’s first solar panel recycling plant in France.

As the industry matures, we expect to see more innovative recycling technologies and business models emerge. This will not only help manage waste but also create jobs and contribute to a circular economy in the solar sector.
The rise of solar panel recycling presents both challenges and opportunities. To address these effectively, it’s essential to understand the current methods used in solar panel recycling. Let’s explore these processes in the next section.
How We Recycle Solar Panels
At Spinifex Energy, we often receive questions about the solar panel recycling process. This complex procedure involves several steps to recover valuable materials and safely dispose of hazardous components.
Mechanical Recycling: Breaking It Down
The recycling process starts with mechanical separation. Workers dismantle panels, remove the aluminum frame and junction box. The remaining panel is crushed and shredded into small pieces. This process separates the glass (about 75% of the panel’s weight) from other materials.
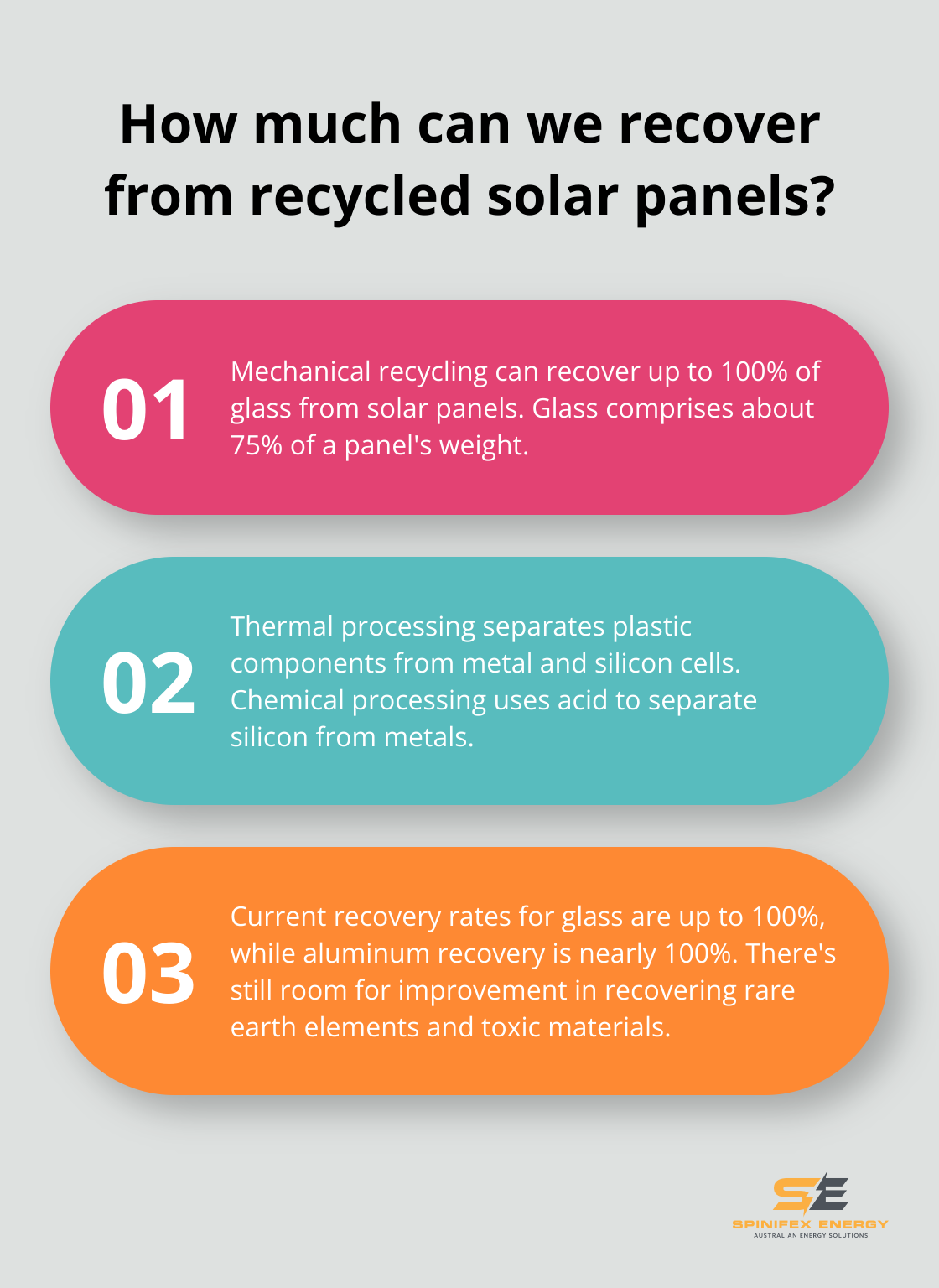
Recent research shows that mechanical recycling can recover up to 100% of the glass from solar panels. Manufacturers use this recovered glass in new solar panels or other glass products, which reduces the need for raw materials.
Thermal and Chemical Processes: Extracting Value
After mechanical separation, thermal and chemical processes extract more valuable materials. Thermal processing heats the remaining materials to separate plastic components from metal and silicon cells.
Chemical processing follows. Workers treat silicon cells with acid to separate silicon from metals.
Recovery Rates: A Success Story in Progress
As recycling technologies advance, recovery rates for different materials in solar panels improve. Current recovery rates include:
- Glass: Up to 100%
- Aluminum: Nearly 100%
These rates impress, but room for improvement remains, especially for rare earth elements and some toxic materials.
The Future of Solar Panel Recycling
The solar industry’s maturation brings exciting developments in recycling technologies. For example, a recent report recommends establishing large waste facilities in five major Australian cities to deal with PV waste.
The recycling process for solar panels requires complexity but offers essential benefits. As we install more solar panels, we must develop and improve our recycling capabilities. This approach will ensure that solar energy remains a truly sustainable solution for our energy needs.
In the next section, we’ll explore the challenges and opportunities that arise from the growing need for solar panel recycling.
Overcoming Recycling Hurdles
Economic Viability: A Balancing Act
The solar panel recycling industry faces significant challenges in terms of economic viability. In Australia, recycling a solar panel costs approximately $28, compared to $4.50 for landfill disposal. This cost disparity discourages widespread adoption of recycling practices.

However, the future looks promising. The Australian PV Institute projects that by 2033, the total material value from end-of-life solar panels in Australia will exceed $1 billion. This potential value creates a strong incentive for recycling initiatives and may tip the scales towards economic feasibility.
Technological Advancements: Innovations in Recycling
Innovative recycling techniques address the complexities of solar panel composition. The ReProSolar project, led by Veolia, works to industrialize solar panel recycling and improve the recovery of valuable components like silver and silicon.
Robotic disassembly and advanced chemical processes show promise in increasing efficiency and reducing costs. These technologies not only improve material recovery rates but also make the recycling process more economically attractive.
Regulatory Landscape: Policy Drives Change
Government policies play a key role in promoting solar panel recycling. Victoria banned e-waste, including solar panels, from landfills on 1 July 2019 under the Waste Management Policy. South Australia and the Australian Capital Territory implement similar restrictions.
The Federal Government’s proposed product stewardship model aims to shift the cost of solar panel recycling from users to producers and importers. This approach will likely drive more stringent recycling standards and encourage manufacturers to design panels with easier end-of-life processing in mind.
Industry Response: Adapting to New Realities
As regulations evolve, businesses and consumers need to stay informed about their responsibilities regarding solar panel disposal and recycling. Companies in the solar industry (such as Spinifex Energy) work to help clients navigate these changing requirements and implement sustainable practices.
The solar panel recycling industry faces challenges, but it also presents opportunities for innovation and growth. As the industry matures, we expect to see more innovative solutions that will make recycling not just environmentally necessary, but economically attractive as well.
Final Thoughts
The rapid growth of solar energy presents opportunities and challenges for commercial solar panel recycling. Manufacturers must design panels with recycling in mind to improve end-of-life processing efficiency. Policymakers should create regulations and incentives that encourage responsible disposal and recycling practices. Consumers can drive demand for environmentally friendly practices by choosing solar providers who prioritize sustainability.

The future of commercial solar panel recycling looks promising as technology advances and economies of scale improve. We expect recycling to become more cost-effective and widespread, contributing to a more circular economy in the solar industry. This shift will minimize waste and maximize the reuse of valuable materials from decommissioned panels.
At Spinifex Energy, we help businesses navigate the complexities of solar energy, including end-of-life considerations. Our energy consulting services optimize electricity expenses and promote sustainable practices (including proper panel disposal). Businesses can contribute to a more sustainable future while enjoying the benefits of solar energy by choosing partners who prioritize the full lifecycle of solar panels.

